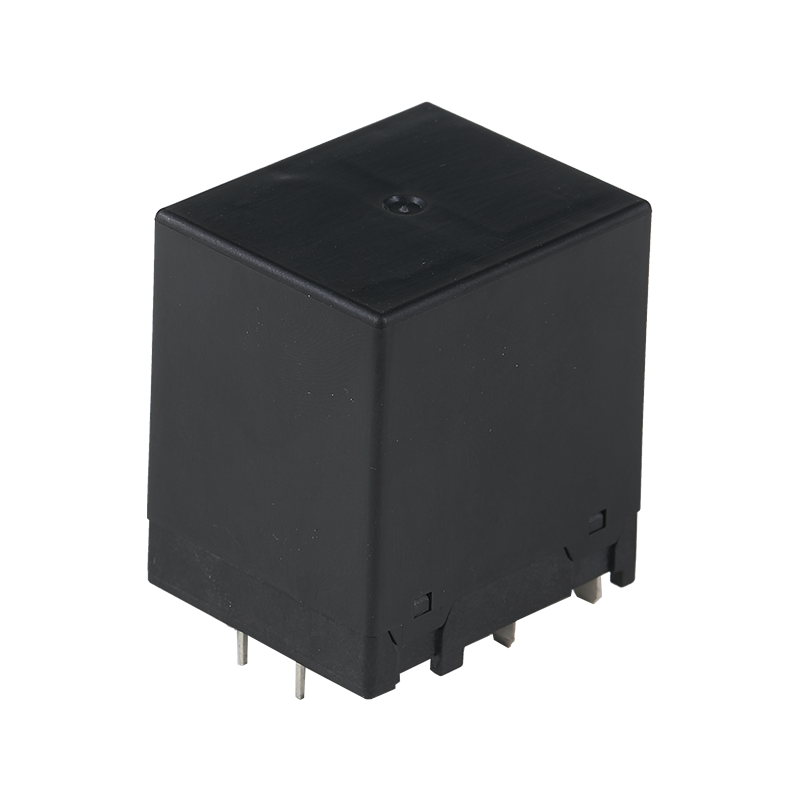
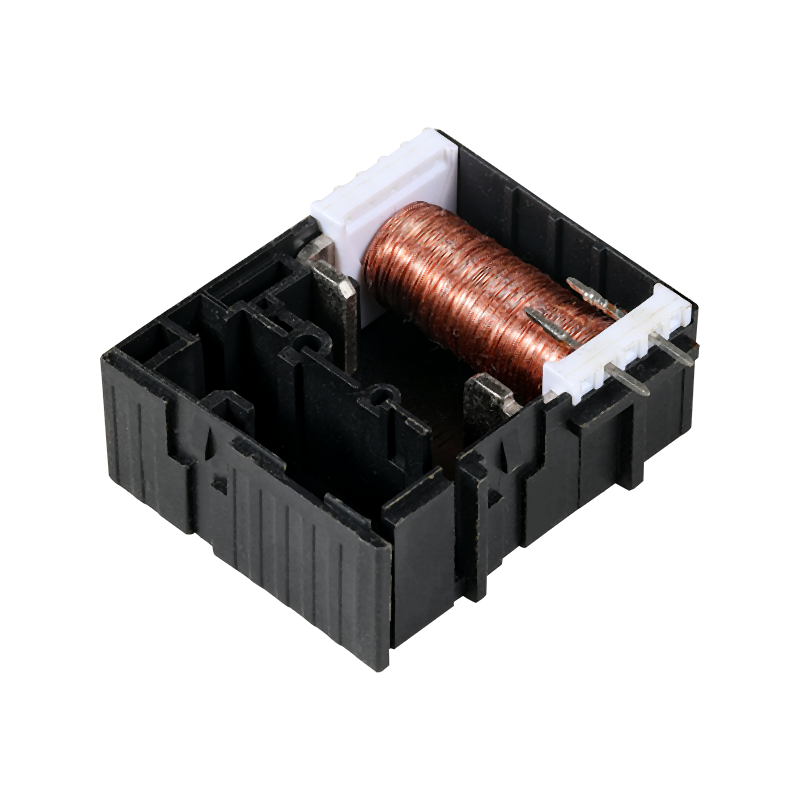
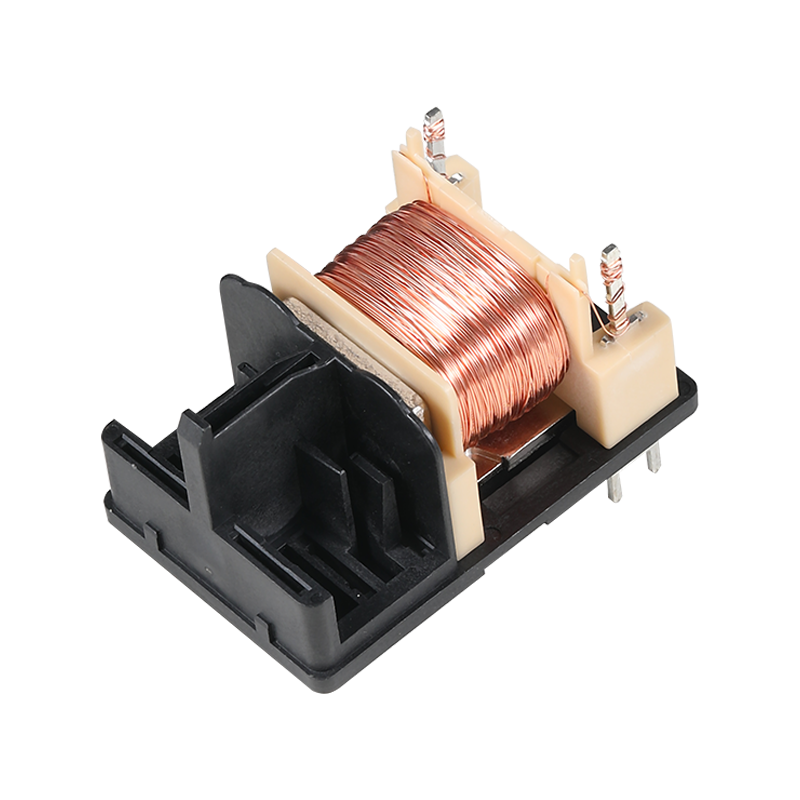
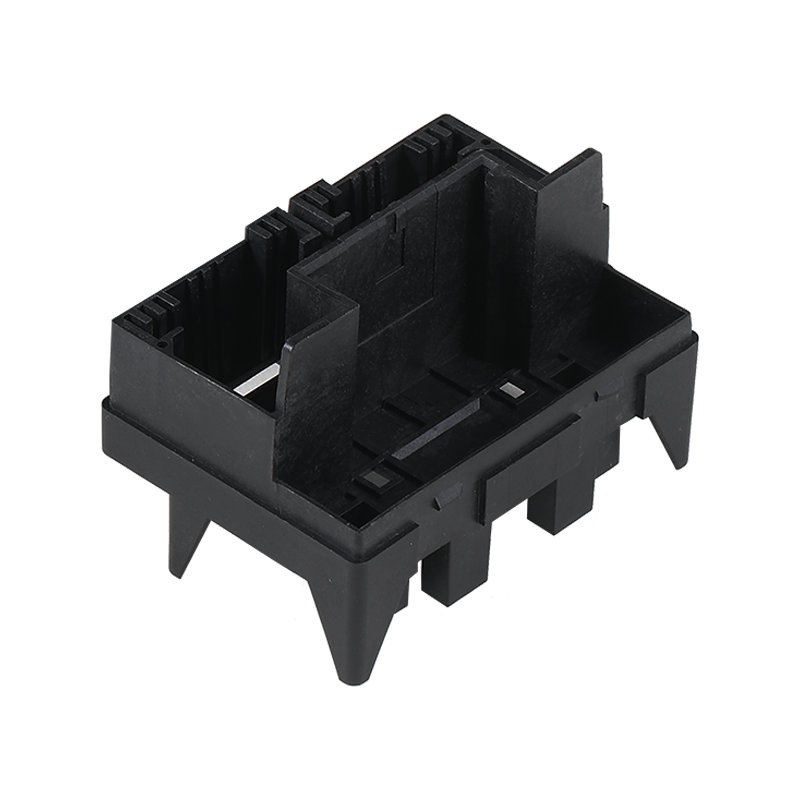
The global industrial landscape relies fundamentally on electric motors to drive machinery, pumps, conveyors, and countless automated processes. Ensuring the reliable and safe operation of these motors is paramount to productivity and asset protection. Central to this safeguarding role is the Motor Magnetic Thermal Overload Protection Relay, a specialized electrical device designed to continuously monitor a motor's operating conditions and interrupt power in the event of potentially damaging faults. This component represents a mature but continuously refined technology, serving as an indispensable protective element in motor control centers, starter panels, and industrial equipment worldwide. Its function is critical for preventing motor burnouts, reducing downtime, and mitigating fire risks associated with electrical overloads.
The Motor Magnetic Thermal Overload Protection Relay operates by monitoring two primary fault conditions: overload and phase failure. The "thermal" element protects against sustained overloads—situations where a motor draws excessive current over a period of time, pilot to dangerous overheating of its windings. This protection is typically achieved through a bimetallic strip or an electronic thermal model that simulates the motor's heating and cooling characteristics. When the simulated temperature exceeds a safe threshold, the relay trips. The "magnetic" element, conversely, provides instantaneous protection against short-circuit conditions—a sudden, massive current surge that requires immediate interruption to prevent catastrophic damage. By integrating both time-delayed thermal and instantaneous magnetic tripping functions into one unit, the Motor Magnetic Thermal Overload Protection Relay offers comprehensive protection against the lots of common electrical faults that threaten motor integrity.
Modern advancements have significantly evolved the traditional Motor Magnetic Thermal Overload Protection Relay. While electromechanical versions remain in widespread use for their simplicity and robustness, electronic or digital relays are becoming increasingly prevalent. These advanced versions utilize microprocessors and current transformers to provide more precise, adjustable, and feature-rich protection. A modern electronic Motor Magnetic Thermal Overload Protection Relay often includes a digital display for real-time current monitoring, highly configurable trip classes (e.g., Class 10, 20, 30) to match the motor's starting characteristics, and protection against other fault conditions like phase unbalance and phase loss, which can also cause harmful motor heating. This shift towards intelligence and programmability allows for closer matching of protection to the specific motor's needs, improving both safety and operational flexibility.
The integration of the Motor Magnetic Thermal Overload Protection Relay into broader industrial networks and the Internet of Things (IoT) represents a key trend. Newer "smart" relays are equipped with communication capabilities, such as Modbus, Profibus, or Ethernet/IP, allowing them to transmit operational data—like motor current, thermal capacity used, and trip logs—to centralized control systems. This facilitates predictive maintenance, as trends in motor loading can be analyzed to foresee problems before a failure occurs. Furthermore, the development of more compact designs and integrated packages that combine the protection relay with contactors and other control devices in single units simplifies panel design and installation. As industrial automation advances and the focus on energy efficiency and predictive analytics intensifies, the Motor Magnetic Thermal Overload Protection Relay will continue to evolve from a simple protective device into a smart, connected node within the industrial ecosystem, maintaining its vital role in protecting one of industry's lots of fundamental assets: the electric motor.
 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский